Table of Contents
This section explains how to add a VBA file containing functions or macros to an libxlsxwriter workbook.
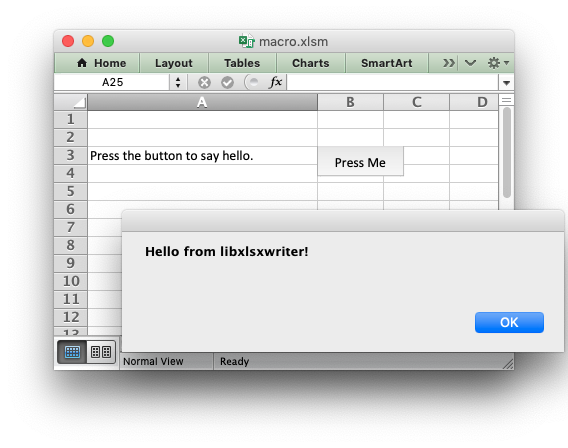
The Excel XLSM file format
An Excel xlsm file is exactly the same as an xlsx file except that is contains an additional vbaProject.bin file which contains functions and/or macros. Excel uses a different extension to differentiate between the two file formats since files containing macros are usually subject to additional security checks.
How VBA macros are included in libxlsxwriter files
The vbaProject.bin file is a binary OLE COM container. This was the format used in older xls versions of Excel prior to Excel 2007. Unlike all of the other components of an xlsx/xlsm file the data isn't stored in XML format. Instead the functions and macros as stored as a pre-parsed binary format. As such it wouldn't be feasible to define macros and create a vbaProject.bin file from scratch (at least not in the remaining lifespan and interest levels of the author).
Instead a workaround is used to extract vbaProject.bin files from existing xlsm files and then add these to libxlsxwriter generated files.
The vba_extract.py utility
The vba_extract.py Python utility is used to extract the vbaProject.bin binary from an Excel 2007+ xlsm file. The utility is included in the libxlsxwriter examples directory:
$ python examples/vba_extract.py macro_file.xlsm Extracted: vbaProject.bin
You can also install vba_extract.py into your system path by installing the Python xlsxwriter module:
$ pip install xlsxwriter ... $ vba_extract.py Utility to extract a vbaProject.bin binary from an Excel 2007+ xlsm macro file ...
If the VBA project is signed, vba_extract.py also extracts the vbaProjectSignature.bin file from the xlsm file. For adding a VBA project signature see Adding signed VBA macros to a libxlsxwriter file.
Adding the VBA macros to a libxlsxwriter file
Once the vbaProject.bin file has been extracted it can be added to the libxlsxwriter workbook using the workbook_add_vba_project() function:
- Note
- The name doesn't have to be
vbaProject.bin. Any suitable path/name for an existing VBA bin file will do.
If the VBA file contains functions you can then refer to them in calculations using worksheet_write_formula():
Excel files that contain functions and macros should use an xlsm extension or else Excel will complain and possibly not open the file:
It is also possible to assign a macro to a button that is inserted into a worksheet using the worksheet_insert_button() function:
See the full example at macro.c.
It may be necessary to specify a more explicit macro name prefixed by the workbook VBA name as follows:
- Note
- Button is the only VBA Control supported by libxlsxwriter and due to the implementation effort required it is unlikely that any other form elements will be added in the future.
Setting the VBA codenames
VBA macros generally refer to workbook and worksheet objects. If the VBA codenames aren't specified explicitly then libxlsxwriter will use the Excel defaults of ThisWorkbook and Sheet1, Sheet2 etc.
If the macro uses other codenames you can set them using the workbook_set_vba_name() and worksheet_set_vba_name() functions as follows:
- Note
- This step is particularly important for macros created with non-English versions of Excel.
You can find the names that are used in the VBA editor or by unzipping the xlsm file and grepping the files. The following shows how to do that using libxml's xmllint to format the XML for clarity:
$ unzip myfile.xlsm -d myfile $ xmllint --format `find myfile -name "*.xml" | xargs` | grep "Pr.*codeName" <workbookPr codeName="MyWorkbook" defaultThemeVersion="124226"/> <sheetPr codeName="MySheet1"/>
- Note
- This step is particularly important for macros created with non-English versions of Excel.
Adding signed VBA macros to a libxlsxwriter file
VBA macros can be signed in Excel to allow for blocking execution of unsigned macros in certain environments, for example.
The vba_extract.py utility can be used to extract the vbaProject.bin and vbaProjectSignature.bin files from an existing xlsm file with signed macros.
To add these files to the libxlsxwriter workbook use the workbook_add_signed_vba_project() function:
- Note
- The names don't have to be
vbaProject.binandvbaProjectSignature.bin. Any suitable paths/names for existing VBA project or signature files will do.
What to do if it doesn't work
The libxlsxwriter test suite contains several tests to ensure that this feature works and there is a working example as shown above. However, there is no guarantee that it will work in all cases. Some effort may be required and some knowledge of VBA will certainly help. If things don't work out here are some things to try:
- Start with a simple macro file, ensure that it works and then add complexity.
- Check the code names that macros use to refer to the workbook and worksheets (see the previous section above). In general VBA uses a code name of
ThisWorkbookto refer to the current workbook and the sheet name (such asSheet1) to refer to the worksheets. These are the defaults used by libxlsxwriter. If the macro uses other names, or the macro was extracted from an non-English language version of Excel, then you can specify the appropriate names using theworkbook_set_vba_name()andworksheet_set_vba_name()functions:// Set the VBA codenames for the workbook and any worksheets.workbook_set_vba_name (workbook, "MyWorkbook");worksheet_set_vba_name(worksheet, "MySheet1");worksheet_set_vba_name(worksheet, "MySheet2"); - Try to extract the macros from an Excel 2007 file. The method should work with macros from later versions (it was also tested with Excel 2010 macros). However there may be features in the macro files of more recent version of Excel that aren't backward compatible.
Next: Example Programs