Table of Contents
The main functions and properties used to add formatting to a cell are shown in The Format object. This section provides some additional information about working with formats.
Creating and using a Format object
Formats are created by calling the workbook_add_format() method and properties as set using the various functions shown below:
Once a Format object has been created and its properties have been set it can be passed as an argument to the worksheet_write*() methods as follows:
Formats can also be passed to the worksheet worksheet_set_row() and worksheet_set_column() methods to define the default formatting properties for a row or column:
Format methods and Format properties
The following table shows the Excel format categories and the equivalent libxlsxwriter Format function:
Format Colors
Format property colors are specified using a Html style RGB integer value or a limited number of defined colors:
See see Working with Colors for more details.
Format Defaults
The default Excel 2007+ cell format is Calibri 11 with all other properties off.
In general a format function call without an argument will turn a property on, for example:
Modifying and Reusing Formats
Once a format has been created it can be used and reused in worksheet_write*() functions across any number of worksheets:
However, each unique cell format in an libxlsxwriter spreadsheet must have a corresponding Format object. It isn't possible to use a Format with a worksheet_write*() method and then redefine it for use at a later stage. This is because a Format is applied to a cell not in its current state but in its final state. Consider the following example:
Cell (0, 0) is assigned a format which with the font set to bold. However, the italic property is subsequently and used in cell (1, 0). This has the effect of adding italic to any previous uses of format. The result in this case is that "Hello" and "World" will both appear as bold and italic.
Number Format Categories
The format_set_num_format() function shown below, is used to set the number format for numbers used with worksheet_write_number():
If the number format you use is the same as one of Excel's built in number formats then it will have a number category such as "General", "Number", "Currency", "Accounting", "Date", "Time", "Percentage", "Fraction", "Scientific", "Text", "Special or "Custom". In the case of the example above the formatted output shows up as a Number category: @image html currency_format1.png If we wanted it to have a different category, such as Currency, then we would have to match the number format string with the number format used by Excel. The easiest way to do this is to open the Number Formatting dialog in Excel and set the format that you want: @image html currency_format2.png Then, while still in the dialog, change to Custom. The format displayed is the format used by Excel. @image html currency_format3.png If we put the format that we found (<tt>"[$$-409]#,##0.00"</tt>) into our previous example and rerun it we will get a number format in the Currency category: @code include "xlsxwriter.h" int main() { lxw_workbook *workbook = workbook_new("currency_format.xlsx"); lxw_worksheet *worksheet = workbook_add_worksheet(workbook, NULL); lxw_format *currency_format = workbook_add_format(workbook); format_set_num_format(currency_format, "[$$-409]#,##0.00"); worksheet_write_number(worksheet, 0, 0, 1234.56, currency_format); workbook_close(workbook); return 0; } @endcode Here is the output: @image html currency_format4.png The same process can be used to find format strings for "Date" or "Accountancy" formats. @section ww_formats_locale Number Formats in different locales As shown in the previous section the <tt>format_set_num_format()</tt> method is used to set the number format for libxlsxwriter formats. A common use case is to set a number format with a "grouping/thousands" separator and a "decimal" point: @code include "xlsxwriter.h" int main() { lxw_workbook *workbook = workbook_new("number_format.xlsx"); lxw_worksheet *worksheet = workbook_add_worksheet(workbook, NULL); lxw_format *number_format = workbook_add_format(workbook); format_set_num_format(number_format, "#,##0.00"); worksheet_write_number(worksheet, 0, 0, 1234.56, number_format); workbook_close(workbook); return 0; } @endcode In the US locale (and some others) where the number "grouping/thousands" separator is "," and the "decimal" point is "." this would be shown in Excel as: @image html currency_format5.png In other locales these values may be reversed or different. They are generally set in the "Region" settings of Windows or Mac OS. Excel handles this by storing the number format in the file format in the US locale, in this case <tt>\#,\#\#0.00</tt>, but renders it according to the regional settings of the host OS. For example, here is the same, unmodified, output file shown above in a German locale: @image html currency_format6.png And here is the same file in a Russian locale. Note the use of a space as the "grouping/thousands" separator:
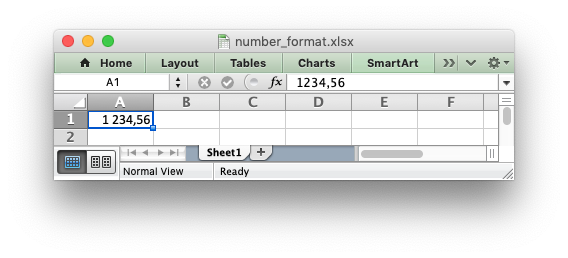
In order to replicate Excel's behavior all XlsxWriter programs should use US locale formatting which will then be rendered in the settings of your host OS.
Next: Working with Colors